Retinal diseases can have a profound impact on a person’s vision and quality of life. Understanding these diseases, recognizing their symptoms, and receiving early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the condition effectively. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of retinal diseases and how they can be navigated for optimal outcomes.
Understanding Retinal Diseases
The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye, playing a vital role in the process of vision. Retinal diseases refer to a wide range of conditions that affect the functioning of the retina. These diseases can impair sight and, if left untreated, may lead to vision loss or even blindness.
Retinal diseases are a complex group of disorders that can impact individuals of all ages, from children to the elderly. They can be caused by various factors, including genetics, aging, underlying health conditions, and environmental influences. Understanding the different types of retinal diseases and their symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management.
What are Retinal Diseases?
Retinal diseases encompass various disorders, including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, retinitis pigmentosa, and macular edema, among others. Each of these conditions affects different parts of the retina and may have different causes and progression patterns.
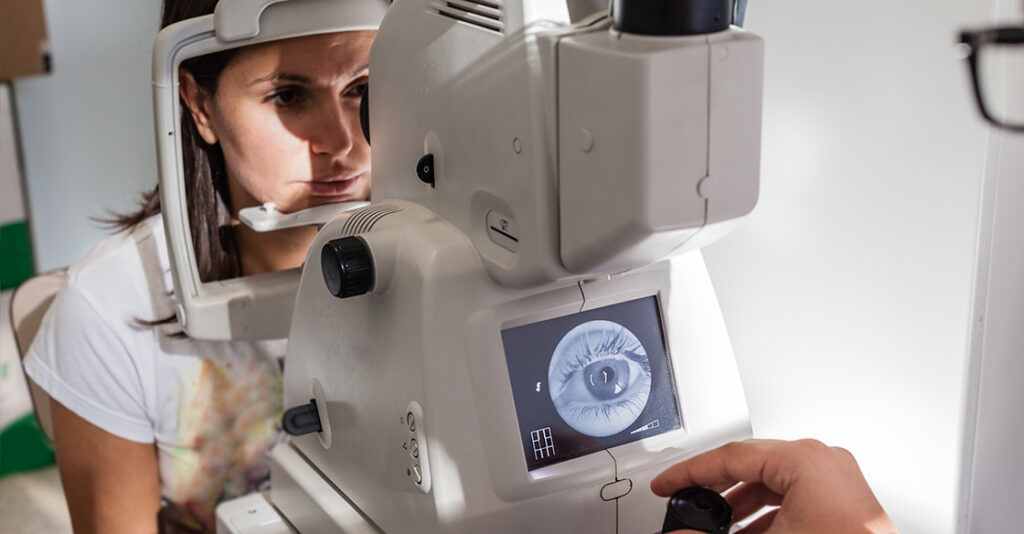

Common Types of Retinal Diseases
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the most common retinal diseases, particularly among older adults. It primarily affects the macula, which is responsible for central vision. Diabetic retinopathy, on the other hand, is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina and is prevalent among individuals with diabetes.
Retinal detachment occurs when the retina is lifted or pulled away from its normal position, leading to vision loss. Retinitis pigmentosa is a genetic disorder that progressively damages the retina, resulting in night blindness and tunnel vision. Macular edema refers to the swelling of the macula due to fluid accumulation, causing distorted or blurred vision. Read more about genetic disorder at https://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/disorders/
It is essential for individuals with retinal diseases to undergo regular eye examinations to monitor their condition and prevent further vision loss. Treatment options for retinal diseases vary depending on the specific disorder and may include medications, laser therapy, or surgical interventions. Early diagnosis and intervention play a critical role in preserving vision and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by retinal diseases.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Early detection of retinal diseases is essential for prompt treatment and better prognosis. Recognizing the warning signs can help individuals seek medical attention and intervention in a timely manner.
Regular eye exams are crucial in detecting retinal diseases early. These exams can help identify any abnormalities in the retina before symptoms manifest, allowing for timely intervention and management. By scheduling routine eye check-ups, individuals can proactively monitor their eye health and address any potential issues promptly.
Early Warning Signs of Retinal Diseases
The warning signs of retinal diseases may vary depending on the specific condition. However, common symptoms include blurred or distorted vision, difficulty seeing in low light conditions, blind spots, floaters, and sudden flashes of light. It is crucial to pay attention to any changes in vision and promptly consult an ophthalmologist for further evaluation.
In addition to the physical symptoms, individuals with retinal diseases may also experience emotional challenges. Vision loss or impairment can have a significant impact on mental health, leading to feelings of frustration, anxiety, or even depression. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or counselors can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of living with a retinal disease.
Progression of Symptoms
While the symptoms of retinal diseases can differ, they often progress over time. Initially, individuals may experience mild visual disturbances that gradually worsen. If left unaddressed, these symptoms can significantly impact daily activities, such as reading, driving, or recognizing faces.
As retinal diseases progress, individuals may also notice changes in color perception or an increased sensitivity to light. These additional symptoms can further affect daily functioning and quality of life. It is important for individuals experiencing such changes to communicate openly with their healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive care and support.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis plays a vital role in managing retinal diseases effectively. Regular eye check-ups and advanced diagnostic techniques enable healthcare professionals to identify retinal diseases at an early stage, allowing for timely intervention.
Timely detection of retinal diseases is crucial for preserving vision and preventing irreversible damage to the delicate tissues of the eye. By catching these conditions early, treatment options are more effective, and the progression of the disease can be slowed or halted.
Role of Regular Eye Check-ups
Scheduling regular eye check-ups is crucial, especially for individuals at higher risk of retinal diseases, such as those with a family history of retinal disorders or certain systemic conditions like diabetes. During these check-ups, ophthalmologists may perform comprehensive eye exams, including visual acuity tests, dilated eye exams, and imaging studies to assess the retina’s health. To read more about diabetes click here.
Regular eye exams not only help in the early detection of retinal diseases but also provide valuable insights into overall eye health. Ophthalmologists can detect other eye conditions like glaucoma, cataracts, or macular degeneration during these routine check-ups, allowing for prompt treatment and management.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Advancements in diagnostic techniques have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of identifying retinal diseases. Optical coherence tomography (OCT), for instance, uses light waves to create detailed cross-sectional images of the retina, helping doctors visualize any abnormalities. Fluorescein angiography and electroretinography are other valuable tools that aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of retinal diseases.
These advanced diagnostic tools not only assist in the early diagnosis of retinal diseases but also play a crucial role in monitoring the progression of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. By tracking changes in the retina over time, healthcare professionals can adjust treatment plans accordingly, ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients.
Treatment Options for Retinal Diseases
Effective treatment options for retinal diseases aim to slow down the progression of the condition, alleviate symptoms, and preserve vision whenever possible. The choice of treatment depends on the specific retinal disease, its severity, and individual factors.
Retinal diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the delicate tissue at the back of the eye responsible for capturing light and sending visual signals to the brain. These conditions can include age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, and retinitis pigmentosa, among others. Each of these diseases presents unique challenges and may require tailored treatment approaches to address them effectively.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments are often used as a first line of defense against retinal diseases. These may include medication therapies, such as intravitreal injections that deliver drugs directly into the eye, or laser therapy to target abnormal blood vessels or seal retinal tears. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as managing blood sugar levels or quitting smoking, may also be recommended to prevent or manage retinal diseases.
Additionally, nutritional supplements containing vitamins and minerals like lutein, zeaxanthin, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids have shown promise in supporting retinal health and slowing disease progression. These supplements can complement other treatment modalities and promote overall eye wellness.
Surgical Interventions
Some retinal diseases may require surgical intervention to restore or preserve vision. Surgical procedures like vitrectomy, retinal detachment repair, or implantation of retinal prostheses may be performed by experienced ophthalmic surgeons. These interventions aim to repair or replace damaged retinal tissues and optimize visual outcomes.
Vitrectomy, for example, involves removing the vitreous gel from the center of the eye to address issues such as vitreous hemorrhage or epiretinal membranes. Retinal detachment repair typically involves reattaching the detached retina to its underlying tissue to prevent permanent vision loss. Implantation of retinal prostheses, also known as bionic eyes, can help restore limited vision in individuals with severe retinal degeneration.
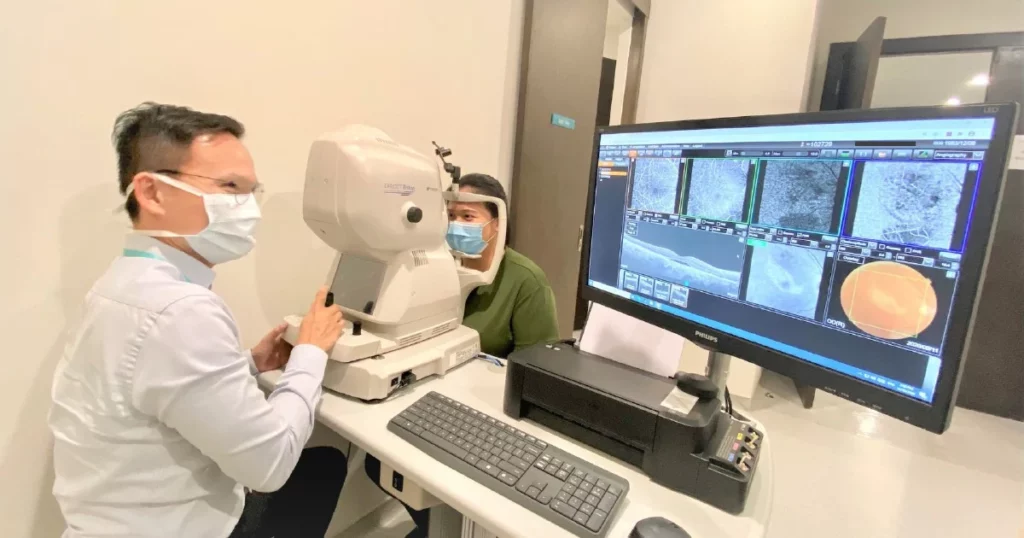

Living with Retinal Diseases
Coping with retinal diseases requires adjustments and adaptations to accommodate visual impairments. While each condition may present unique challenges, certain lifestyle modifications and support systems can enhance the quality of life for individuals with retinal diseases.
Retinal diseases encompass a range of conditions affecting the retina, the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye. These diseases can lead to vision loss and impact daily activities, such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces. Managing these challenges often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including ophthalmologists, low vision specialists, and occupational therapists.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to better overall eye health and manage the progression of retinal diseases. This may include eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, maintaining a regular exercise routine, and protecting the eyes from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation by wearing sunglasses and hats.
In addition to these lifestyle changes, individuals with retinal diseases may benefit from assistive devices and technologies designed to improve visual function. These can range from magnifiers and high-contrast tools to screen-reading software and wearable devices that provide audio cues for navigation.
Support and Resources for Patients
Living with a retinal disease can be emotionally and psychologically challenging. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, patient support groups, and online resources can provide individuals with a platform to connect with others facing similar experiences. These networks offer valuable guidance, coping strategies, and the opportunity to share personal journeys.
Furthermore, staying informed about the latest research and treatment options for retinal diseases is crucial. Clinical trials, genetic testing, and emerging therapies hold promise for improving outcomes and slowing disease progression. Engaging with healthcare providers to explore these opportunities can empower individuals to take an active role in managing their condition.
By understanding retinal diseases, recognizing their symptoms, seeking early diagnosis, and accessing appropriate treatments, individuals can effectively navigate the challenges of these conditions. With proper care, support, and lifestyle modifications, it is possible to optimize visual outcomes and preserve quality of life for those living with retinal diseases.
Read more: The Role of a Retinal Specialist in Managing Eye Health